Disclaimer: migweldercart.com provides industry expertise and research to its readers. You help us by using the links to our carefully picked items, which may earn us a little commission.
A MIG welder is a welding machine used for MIG welding. This welding method joins two metal parts using a wire lead that is used up and a shielding gas. Popular because it is a quick, efficient, and versatile method that can be applied to various projects. It is commonly used for welding steel, aluminum, and stainless steel in industrial contexts. The machine has a power source, a wire feed system, and a shielding gas system, and it is simple to learn and operate.
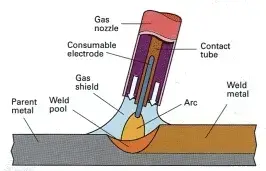
MIG (Metal Inert Gas) welding, or Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW), is a welding process that uses an electric arc between a wire lead that is used up and the workpiece to join two or more pieces of metal together.
MIG welding is a versatile and efficient process commonly used in industrial, automotive, and fabrication applications.
MIG welding is a versatile and efficient process commonly used in industrial, automotive, and fabrication applications.
During the MIG welding process, a shielding gas, usually a mixture of argon and carbon dioxide, protects the weld pool from atmospheric contamination. The consumable wire electrode is continuously fed through a welding gun. It melts as it contacts the workpiece, creating a molten pool that cools and solidifies to form the welded joint.
MIG welding is famous for its speed, ease of use, and ability to produce high-quality welds. It is commonly used for welding mild steel, stainless steel, aluminum, and other metals and alloys.
To perform MIG welding, a welding machine, a welding gun, a wire feeder, and a shielding gas source are required. The welding machine provides the electric current necessary for welding, the wire feeder controls the speed at which the wire is fed into the weld pool, and the shielding gas source provides the protective atmosphere for the weld pool.
MIG welding can be performed in various positions, including flat, horizontal, vertical, and overhead. Selecting the correct wire size, welding parameters, and shielding gas mixture for the specific application is essential to ensure a successful weld.
A MIG (Metal Inert Gas) welder, also known as a Gas Metal Arc Welder (GMAW), is a welding machine that uses an electric arc to combine two or more pieces of metal.
The MIG welding process involves feeding a continuous spool of consumable wire electrodes through a welding gun, which melts and joins the welded metals.

MIG welders are commonly used in industrial, automotive, and fabrication applications. They are preferred for their versatility and ease of use. They can be used to weld various metals, including mild steel, stainless steel, and aluminum.
MIG welders consist of several components: a power source, a wire feeder, a welding gun, and a shielding gas source. The power source provides the electric current necessary for welding. At the same time, the wire feeder controls the speed at which the wire is fed into the weld pool. Finally, the welding gun directs the wire and shielding gas to the weld pool, and the shielding gas source provides the protective atmosphere for the weld pool.
MIG welders can be used for welding in various positions, including flat, horizontal, vertical, and overhead. They are preferred for their ability to produce high-quality welds quickly and efficiently and for their ease of use, making them suitable for professional and amateur welders.
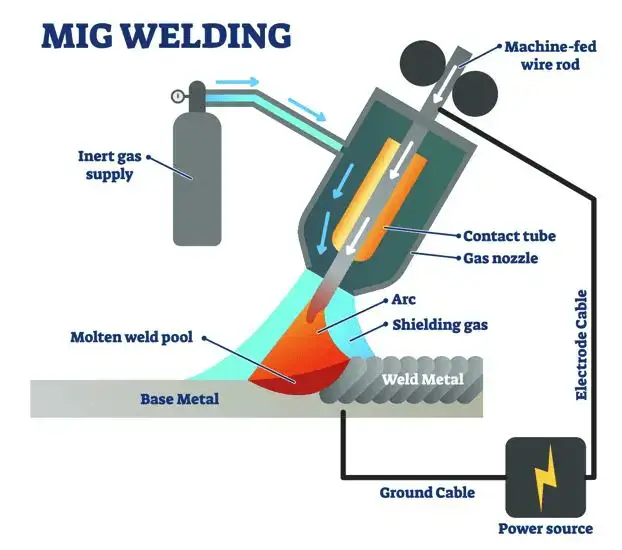
MIG welding is an arc welding process that uses a wire lead that is used up and shielding gas to combine two or more pieces of metal. The wire electrode is fed through a welding gun, which the welder holds.
As the wire comes into contact with the metal, an electric arc is created between the electrode and the workpiece.
The arc melts the wire and the metal, creating a molten pool of metal that cools and solidifies to form a weld joint. The shielding gas, released through the welding gun, protects the weld from atmospheric contamination and helps produce a clean, strong weld.
MIG welding is commonly used in industrial settings because of its efficiency, versatility, and ease of use. It is a relatively fast welding process and can be used to weld various metals, including steel, stainless steel, aluminum, and copper alloys.
One of the benefits of MIG welding is its versatility. The process can produce both thin and thick welds and be used in various positions, including flat, horizontal, vertical, and overhead.
Another advantage of MIG welding is that it produces a smooth, clean weld with little spatter, making it a popular choice for applications where appearance is essential.
Overall, MIG welding is a reliable and efficient welding process that can produce high-quality welds with minimal skill and experience. As a result, it is widely used in the manufacturing and construction industries and automotive and aerospace applications.

MIG welding was developed in the 1940s as a response to the need for a faster and more efficient welding process in the manufacturing industry. The process was initially known as gas metal arc welding (GMAW).
It was developed independently by several researchers in different countries.
In the United States, the process was developed by the Battelle Memorial Institute; in the UK, it was developed by the Welding Institute. In the Soviet Union, the process was developed by V.I. Kucherenko and his team.
The first practical application of MIG welding was in the aircraft manufacturing industry, which was used for welding thin aluminum sheets. The process quickly gained popularity due to its high productivity, clean welds, and ease of use.
Over time, MIG welding became more widely used in other industries, such as automotive, construction, and shipbuilding. In addition, developing new welding machines, welding wires, and shielding gases further improved the process and made it more versatile and efficient.
Today, MIG welding is one of the most popular welding processes in the world. It is used in a wide range of industries and applications. Its development and evolution have led to significant advancements in welding technology, making it easier, faster, and more precise than ever before.

Overall, MIG welding is a highly versatile and efficient welding process that can produce high-quality welds quickly and easily. Its benefits make it popular in various industries, from automotive and construction to manufacturing and aerospace.
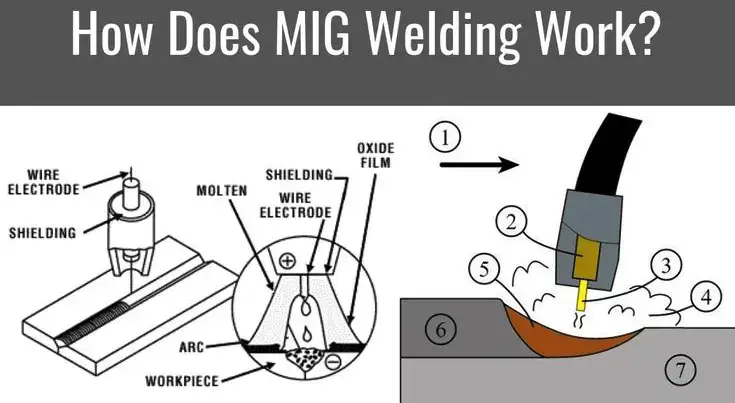
Overall, MIG welding is a simple but highly effective welding process that uses a combination of electricity, heat, and gas to create solid and durable welds quickly and efficiently.
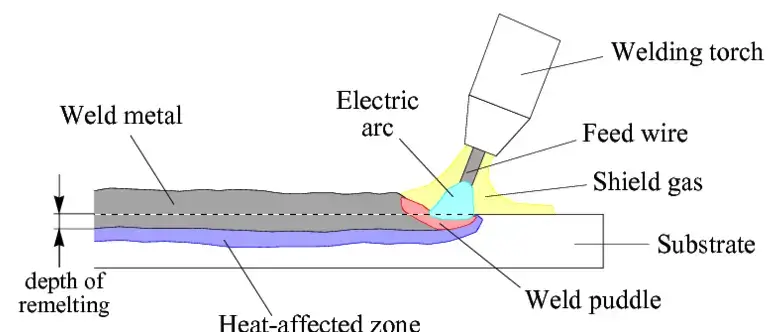
The MIG welding process is a type of gas metal arc welding (GMAW) that uses a continuously fed wire electrode and a shielding gas to create a weld between two pieces of metal. Here’s a step-by-step explanation of the process:
1. Prepare the workpiece: Before beginning the welding process, the workpiece should be cleaned and prepared to ensure a robust and durable weld. This may involve removing any rust or debris from the surface and clamping the pieces in place to prevent movement during welding.
2. Select the appropriate wire electrode and shielding gas: The wire electrode and shielding gas should be chosen based on the type of metal being welded and the desired weld characteristics. For example, different types of wire electrodes may be used for welding steel, stainless steel, or aluminum.
3. Set up the welding machine: The welding machine should be set up according to the manufacturer’s instructions, with the appropriate wire feed speed and voltage settings for the wire electrode being used.
7. Pull the trigger: Once the welding gun is in position, the welder can pull the trigger to start the flow of electricity and begin welding. The wire electrode is fed through the gun and into the welding arc, melting and fusing with the metal being welded.
8. Control the welding speed: The welding gun moving along the workpiece will determine the welding rate and the weld’s overall quality. Therefore, maintaining a consistent pace and angle is essential to create a robust and uniform weld.
9. Finish the weld: Once the welding is complete, the weld can be further finished by grinding or polishing to create a smooth, professional-looking surface.
Overall, the MIG welding process is a relatively simple and versatile welding method that can create solid and durable welds quickly and efficiently. With proper training and experience, welders can use MIG welding to produce high-quality welds on various metals and applications.
MIG welding equipment typically includes the following components:
1. Welding machine: The welding machine is the heart of the MIG welding system. It provides the electrical power to generate the welding arc and control the wire feed speed.
2. Welding gun: The welding gun is the handheld tool that directs the flow of the welding arc onto the workpiece. It includes a trigger for controlling the wire feed and an electrode holder for attaching the wire electrode.
3. Wire feeder: The wire feeder is a separate device used to control the wire feed speed and deliver the wire electrode to the welding gun. It can be mounted on the welding machine or used separately.
4. Wire electrode: The wire electrode is the consumable wire fed through the welding gun and used to create the weld. Depending on the welded metal, it is available in various diameters and types.
5. Shielding gas supply: The shielding gas supply provides the gas used to protect the weld from atmospheric contamination. The gas is typically delivered through a hose connected to the welding gun.
6. Regulator: The regulator is used to control the flow of shielding gas and maintain a constant flow rate throughout the welding process.
7. Ground clamp: The clamp connects the welding machine and the workpiece, ensuring proper grounding and preventing electrical shock.
8. Personal protective equipment (PPE): Welders should always wear appropriate PPE, including a welding helmet, gloves, and a welding jacket, to protect themselves from the welding arc and any sparks or debris produced during welding.
Overall, MIG welding equipment is relatively simple and easy to set up and use, making it a popular choice for professional and DIY welding projects. With proper equipment and training, welders can use MIG welding to create durable welds on various metals and applications.
MIG welding can be a safe process when appropriate safety precautions are followed. Here are some essential safety precautions to keep in mind:
1. Wear appropriate PPE: Always wear proper personal protective equipment (PPE), including a welding helmet with a clear lens shade, gloves, a welding jacket or apron, and safety glasses. The PPE should be flame-resistant and provide adequate coverage and protection.
2. Ventilate the workspace: Welding produces harmful fumes and gases that can be dangerous if inhaled. Ensure the workspace is well-ventilated through natural ventilation or ventilation systems such as fume extractors or exhaust fans.
3. Avoid flammable materials: MIG welding produces sparks and can ignite flammable materials. Keep the workspace clear of combustible materials, including solvents, oil, and gasoline.
4. Keep a fire extinguisher nearby: In case of fire, keep a fire extinguisher nearby and know how to use it.
5. Inspect equipment regularly: Inspect MIG welding equipment, including the welding machine, welding gun, wire feeder, and hoses, for damage or wear. Replace any damaged or worn equipment immediately.
6. Ground the workpiece: Always ground the workpiece to prevent electrical shock and ensure proper grounding during welding.
7. Disconnect power before servicing equipment: Before servicing MIG welding equipment, disconnect the power source to prevent accidental electrical shock.
By following these safety precautions, welders can help ensure a safe and successful MIG welding process.

There are three main types of MIG welders:
1. Flux-cored arc welding (FCAW): This type of MIG welding uses a tubular wire electrode filled with flux. The flux helps protect the weld from atmospheric contamination and provides a shielding gas. FCAW can be used for welding thick materials and is suitable for outdoor welding applications since it is less affected by wind and drafts.
2. Gas metal arc welding (GMAW): This type of MIG welding uses a solid wire electrode and a shielding gas to protect the weld from atmospheric contamination. GMAW produces less spatter and is ideal for welding thinner materials. However, it requires a clean workspace with minimal drafts to prevent the shielding gas from being disrupted.
3. Dual shield welding: MIG welding combines a flux-cored wire electrode and a shielding gas to produce a stronger weld than FCAW or GMAW alone. Dual shield welding is typically used for heavy-duty welding applications, such as shipbuilding or structural steel fabrication.
Each type of MIG welding has advantages and disadvantages. The choice of welding method will depend on the welding application and materials being welded.
MIG welding is a versatile welding process used with various metals and applications. Several types of MIG welders are available, each with advantages and limitations. Here is an overview of the most common types of MIG welders:
1. Portable MIG welders are lightweight and compact for small-scale welding projects and DIY enthusiasts. They are designed for use with a standard 110V household outlet and can be easily transported.
2. Industrial MIG welders: These are heavy-duty welders designed for industrial applications, such as manufacturing, construction, and shipbuilding. They are typically more extensive and powerful than portable welders and can weld thicker materials.
3. Inverter-based MIG welders: These welders use advanced inverter technology to produce a more stable and efficient welding arc. They are ideal for welding thin materials and can be used with various metals, including aluminum and stainless steel.
4. Multiprocess MIG welders: These versatile welders can perform multiple welding processes, such as MIG, TIG, and stick welding. They are ideal for welders working with various metals and need a machine that can handle multiple welding applications.
5. Automated MIG welders: These robotic welding systems are designed for high-volume manufacturing and production applications. They are ideal for welding repetitive parts and can increase productivity and efficiency.
Overall, the choice of MIG welder will depend on the specific welding application, the type of metal being welded, and the skill level of the welder. Therefore, it is essential to select a welder that meets the specific needs of the welding project to ensure a successful weld.
Here is a comparison of the different types of MIG welders:
1. Portable MIG welders: These are lightweight and compact, making them easy to transport and store. They are ideal for small-scale welding projects and DIY enthusiasts. However, they may not have the power to weld thicker materials and may have limitations in terms of welding output.
2. Industrial MIG welders: These are heavy-duty welders that are designed for use in industrial applications. They are larger and more powerful than portable welders and can weld thicker materials. However, they are less mobile and may require a higher voltage power source.
3. Inverter-based MIG welders: These welders use advanced inverter technology to produce a more stable and efficient welding arc. They are ideal for welding thin materials and can be used with various metals, including aluminum and stainless steel. However, they may be more expensive than traditional MIG welders.
4. Multiprocess MIG welders: These versatile welders can perform multiple welding processes, such as MIG, TIG, and stick welding. They are ideal for welders working with various metals and need a machine that can handle multiple welding applications. However, they may be more expensive than traditional MIG welders and require additional training.
5. Automated MIG welders: These robotic welding systems are designed for high-volume manufacturing and production applications. They are ideal for welding repetitive parts and can increase productivity and efficiency. However, they may be costly and require specialized training and programming.
Overall, the choice of MIG welder will depend on the specific welding application, the type of metal being welded, and the skill level of the welder. When selecting a MIG welder, it is essential to consider factors such as portability, power, versatility, and cost.
Here are the advantages and disadvantages of each type of MIG welder:
Advantages:
Disadvantages:
Advantages:
Disadvantages:
Advantages:
Disadvantages:
Advantages:
Disadvantages:
Advantages:
Disadvantages:
Overall, the choice of MIG welder will depend on the specific welding application, the type of metal being welded, and the skill level of the welder. Each type of MIG welder has advantages and disadvantages. It is essential to carefully consider these factors when selecting a MIG welder for a project.
MIG welding is a versatile welding process used in various applications. Here are some typical applications of MIG welding:
1. Automotive industry: MIG welding is commonly used in the automotive industry to join body panels, exhaust systems, and other components. It is also used in the repair and maintenance of vehicles.
2. Construction industry: MIG welding is used in the construction industry to join metal frames, beams, and other structural components. It is also used in the repair and maintenance of buildings and infrastructure.
3. Manufacturing industry: MIG welding is used in the manufacturing industry to join metal parts and components for various products, such as appliances, furniture, and machinery.
4. Shipbuilding industry: MIG welding is used in the shipbuilding industry to join metal plates and components for ships and boats.
5. Aerospace industry: MIG welding is used in the aerospace industry to join metal parts and components for aircraft and spacecraft.
6. DIY projects: MIG welding is also popular among DIY enthusiasts for various projects, such as building custom furniture, welding art pieces, and repairing metal items.
Overall, MIG welding is a versatile and widely used welding process that can be applied in various industries and applications. Its ease of use, versatility, and ability to produce solid and clean welds make it a popular choice for many welding projects.
MIG welding is a widely used welding process that can be applied in various industries and applications. Here is an overview of the different applications of MIG welding:
1. Automotive industry: MIG welding is widely used in the automotive industry to join body panels, exhaust systems, and other components. It is also used in the repair and maintenance of vehicles.
2. Construction industry: MIG welding is used in the construction industry to join metal frames, beams, and other structural components. It is also used in the repair and maintenance of buildings and infrastructure.
3. Manufacturing industry: MIG welding is used in the manufacturing industry to join metal parts and components for various products, such as appliances, furniture, and machinery.
4. Shipbuilding industry: MIG welding is used in the shipbuilding industry to join metal plates and components for ships and boats.
5. Aerospace industry: MIG welding is used in the aerospace industry to join metal parts and components for aircraft and spacecraft.
6. DIY projects: MIG welding is also popular among DIY enthusiasts for various projects, such as building custom furniture, welding art pieces, and repairing metal items.
7. Art and sculpture: MIG welding can also be used to create art and sculptures out of metal.
8. Agricultural equipment: MIG welding is used in the agricultural industry to manufacture and repair equipment such as plows, cultivators, and harvesters.
9. Energy industry: MIG welding is used in the energy industry for manufacturing and maintaining pipelines, storage tanks, and other equipment.
Overall, MIG welding is a versatile welding process that can be applied in various industries and applications, making it a popular choice for many welding projects.
MIG welding is widely used in industrial applications due to its versatility, ease of use, and ability to produce high-quality welds. Here are some typical industrial applications of MIG welding:
1. Manufacturing: MIG welding is widely used in the manufacturing industry for joining metal parts and components for various products, such as automobiles, appliances, furniture, and machinery.
2. Fabrication: MIG welding is commonly used in metal fabrication to create metal structures, frames, and components for buildings, bridges, and other infrastructure.
3. Maintenance and repair: MIG welding is often used for maintenance and repair work in industrial settings, such as repairing machinery and equipment, repairing damaged metal parts, and joining new components to existing structures.
4. Oil and gas industry: MIG welding is used in the oil and gas industry to fabricate and repair pipelines, storage tanks, and other equipment.
5. Aerospace industry: MIG welding is used in the aerospace industry to join metal parts and components for aircraft and spacecraft.
6. Shipbuilding industry: MIG welding is used in the shipbuilding industry to join metal plates and components for ships and boats.
7. Energy industry: MIG welding is used in the energy industry for manufacturing and maintaining pipelines, storage tanks, and other equipment.
8. Heavy equipment: MIG welding is used to manufacture and repair heavy equipment such as bulldozers, cranes, and excavators.
MIG welding is a versatile welding process widely used in industrial applications for joining metal parts and components, fabricating metal structures, and repairing damaged equipment and infrastructure.
MIG welding can also be used in household applications, particularly for DIY projects and repairs. Here are some typical household applications of MIG welding:
1. Furniture: MIG welding can create custom metal furniture, such as chairs, tables, and shelving.
2. Home decor: MIG welding can be used to create metal art pieces, sculptures, and other decorative items for the home.
3. Home repairs: MIG welding can repair damaged metal items, such as appliances, lawn equipment, and tools.
4. Automotive repairs: MIG welding can be used to repair and fabricate metal components for cars and motorcycles.
5. Gardening and landscaping: MIG welding can create metal garden structures, such as trellises, planters, and fencing.
6. DIY projects: MIG welding can be used for various DIY projects, such as building metal structures, repairing metal items, and creating custom artwork.
Overall, MIG welding can be helpful for DIY enthusiasts and homeowners looking to create custom metal items, repair damaged ones, and complete various home projects. However, it is essential to use caution and follow proper safety protocols when using MIG welding equipment.
MIG welding is widely used in the automotive industry because it produces high-quality welds quickly and efficiently. Here are some typical automotive applications of MIG welding:
1. Body repairs: MIG welding is commonly used in body repairs to weld damaged metal panels, replace damaged parts, and fabricate custom parts.
2. Exhaust systems: MIG welding is often used for welding exhaust systems for cars and motorcycles. It can produce high-quality, leak-free welds on thin-walled tubing.
3. Suspension systems: MIG welding fabricates suspension components, such as control arms, subframes, and strut towers.
4. Roll cages: MIG welding fabricates roll cages for race cars and other high-performance vehicles. It can produce strong, durable welds that can withstand the stresses of high-speed impacts.
5. Customizations: MIG welding is often used in customizations, such as lowering or lifting a car’s suspension, adding body modifications, or creating custom exhaust systems.
Overall, MIG welding is a versatile welding process widely used in the automotive industry to repair damaged body panels, fabricate custom parts, and create high-performance components. However, it is essential to use caution and follow proper safety protocols when using MIG welding equipment, especially when working on cars and other vehicles.
Choosing the best MIG welder depends on several factors, such as the operator’s intended use, budget, and skill level.
Here are some key considerations when choosing a MIG welder:

1. Power output: The power output of a MIG welder is measured in amps and determines the thickness of the metal that can be welded. A higher power output is needed for welding thicker metals.
2. Duty cycle: The duty cycle is how long a welder can operate continuously before needing to cool down. A higher duty cycle means more welding time without interruptions.
3. Portability: Consider whether you need a portable MIG welder to move quickly from one job site to another.
4. Voltage input: MIG welders can operate on different voltage inputs, such as 120V or 240V. Consider the voltage in your workspace and choose a welder that voltage can provide power.
5. Wire feeding system: A quality wire feeding system ensures consistent wire speed and helps prevent wire jams or tangles.
6. Welder brand and reputation: Look for a reputable brand with a good reputation for quality and reliability.
7. Price: Consider your budget and choose a welder that offers the best features and performance within your price range.
Overall, the best MIG welder for you will depend on your specific needs and budget. Therefore, researching and choosing a welder that offers the features and performance you need for your intended use is essential.
When choosing a MIG welder, several factors must be considered to ensure you get the best one for your needs. Here are some essential elements to keep in mind:
1. Welding Capacity: The welding capacity of a MIG welder is typically measured in amps, and the higher the amp rating, the thicker the material it can weld. Therefore, make sure to choose a MIG welder with an amperage range suitable for the thickness of the materials you plan to weld.
2. Power Source: MIG welders come in different power sources – some use AC power, while others use DC power. DC-powered MIG welders are more versatile and efficient than AC-powered ones. You may also consider a MIG welder with a built-in inverter for greater flexibility.
3. Wire Feed Speed: Wire feed speed is essential when choosing a MIG welder. It determines the rate at which the welding wire is fed through the gun, affecting the weld’s quality. Look for a MIG welder with adjustable wire feed speed for greater control over the welding process.
4. Portability: If you plan to move your MIG welder around, consider its size, weight, and portability. Look for a model with wheels or a handle to make moving easier.
5. Price: The cost of a MIG welder varies depending on its features and capabilities. Decide on a budget and look for a welder that offers the best value for money.
6. Brand Reputation: Consider the brand reputation and customer service when choosing a MIG welder. Look for a reputable brand with a good track record in producing quality MIG welders and providing excellent customer support.
7. Ease of Use: Choose a MIG welder that is easy to use, with clear instructions and intuitive controls. A user-friendly MIG welder can save you time and frustration in the long run.
Considering these factors, you can choose a MIG welder that best suits your needs and budget.
Here’s a list of the Best MIG Welders in the Market featuring the top 10 picks you provided, along with brief descriptions for each:
ARCCAPTAIN 130A MIG Welder
YESWELDER MIG-205DS
TOOLIOM 135A MIG Welder
YESWELDER 135Amp MIG Welder
Lincoln Electric 90i MIG Welder
Hobart 500553 Handler 210 MVP MIG Welder
Flux Core Mig Welder 110V
BILT HARD 110V MIG Welder
DEKOPRO 110/220V MMA Welder
FORNEY Easy Weld 140 Amp Welder
Each of these MIG welders offers unique features suitable for different welding needs, from beginner-friendly options to more advanced models. Consider factors like power output, versatility, and included accessories when choosing the right welder for your projects.
Maintenance and troubleshooting are crucial to keep your MIG welder running smoothly and producing quality welds. Here are some tips for maintaining and troubleshooting your MIG welder:
Maintenance:
1. Keep your MIG welder clean and free from dirt, dust, and debris. Regularly clean the exterior and interior of the welder.
2. Inspect the welder’s cables, connections, and other parts for wear and tear. Replace any damaged or worn parts immediately.
3. Check the gas supply and ensure the gas cylinder is securely attached and not leaking.
4. Replace the welding wire when it runs out or becomes damaged.
Use suitable consumables for your MIG welders, such as the correct welding wire, contact tips, and nozzle.
Troubleshooting:
1. If your MIG welder is not producing a stable arc, check the welding wire feed and make sure it is not slipping or obstructed.
2. If your welds are not penetrating or are producing excessive spatter, check the wire speed, voltage, and gas flow rate.
3. If the welder is overheating or tripping the circuit breaker, check for any obstructions in the ventilation system or a buildup of dirt and debris.
4. If you experience wire burn-back, the welding wire may stick to the contact tip. Try cleaning or replacing the contact tip.
5. If the gas flow is low or non-existent, check the gas supply and valve to ensure it is open and functioning correctly.
Remember, safety is paramount when troubleshooting and maintaining your MIG welder. Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions and consult a professional if unsure about any repairs or maintenance tasks.
Proper maintenance of a MIG welder ensures its longevity and performance. Here are some tips to help you maintain your MIG welder:
1. Keep your MIG welder clean and free from dirt, dust, and debris. Regularly wipe down the exterior of the welder with a clean, dry cloth, and use a brush to clean any dirt or debris that has accumulated on the interior.
2. Check the welding cables and connections for wear and tear. Replace any damaged or worn-out parts immediately to prevent electrical hazards.
3. Inspect the welding gun, contact tip, and nozzle regularly. Replace the contact tip and nozzle if worn, and clean the weapon periodically to remove any dirt or debris that may have accumulated.
4. Clean the wire feed system regularly to prevent dirt or debris clogging the wire feed rollers or other system parts.
5. Check the gas supply regularly and ensure the gas cylinder is securely attached and not leaking. Replace the gas cylinder as needed.
6. Use the correct welding wire for the job and make sure that the wire is not contaminated with dirt or debris. Store the welding wire in a dry, clean place to prevent rust or corrosion.
7. Check the power cord and regularly plug it in for damage or wear. Replace any damaged cables or plugs immediately to prevent electrical hazards.
Following these maintenance tips, you can keep your MIG welder running smoothly and produce quality welds. Remember to consult the manufacturer’s instructions for specific maintenance requirements and schedule periodic inspections by a professional welder to ensure that your MIG welder is in top condition.
MIG welders can experience various issues that affect their performance and the quality of the welds. Here are some of the most common problems with MIG welders:
1. Poor wire feeding: This can be caused by dirty or damaged wire feed rollers, a worn-out liner, or a clogged or damaged gun nozzle.
2. Burn-back occurs when the welding wire sticks to the contact tip, causing it to melt back into the gun. Incorrect wire speed or voltage settings, a worn-out contact tip, or a dirty or damaged gun nozzle can cause it.
3. Porosity in welds occurs when gas bubbles form in the weld, resulting in small holes. It can be caused by insufficient gas flow, a damaged or clogged gas diffuser or nozzle, or a contaminated welding surface.
4. Excessive spatter occurs when molten metal splatters from the weld pool onto the surrounding area. It can be caused by incorrect voltage or wire speed settings, a contaminated welding surface, or a dirty or damaged gun nozzle.
5. Weld discontinuity occurs when there is a break or lack of fusion in the weld. An improper welding technique, incorrect settings, or a contaminated surface can cause it.
6. Overheating occurs when the MIG welder overheats, causing it to shut down or trip the circuit breaker. It can be caused by a clogged or damaged ventilation system, a dirty or damaged cooling fan, or overloading the welder beyond its capacity.
By understanding these common problems, you can troubleshoot and address them promptly to ensure that your MIG welder performs optimally and produces quality welds. Safety is paramount when troubleshooting and addressing any issues with your MIG welder. Always consult the manufacturer’s instructions and consult a professional if you are unsure about any repairs or maintenance tasks.

Here are some tips for troubleshooting common issues with MIG welders:
1. Poor wire feeding: Check the wire feed rollers for damage and dirt buildup. Ensure the wire is correctly aligned with the rollers and not too loose or tight. Clean or replace the gun nozzle, liner, or contact tip.
2. Burn-back: Check the wire speed and voltage settings to ensure they are correct for the welded material. Clean or replace the contact tip, gun nozzle, or liner. Make sure the wire is trimmed correctly and not too long.
3. Porosity in welds: Check the gas flow and ensure the gas diffuser and nozzle are clean and free of damage or blockage. Clean the welding surface to remove any contaminants.
4. Excessive spatter: Check the voltage and wire speed settings to ensure they are correct for the welded material. Clean the welding surface to remove any contaminants. Replace the gun nozzle or contact tip as necessary.
5. Weld discontinuity: Check your welding technique and settings to ensure they are correct for the welded material. Clean the welding surface to remove any contaminants.
6. Overheating: Check the ventilation system to ensure it is not clogged or damaged. Make sure the cooling fan is working correctly. Reduce the load on the welder or upgrade to a higher-capacity welder if necessary.
Remember, safety is paramount when troubleshooting any issues with your MIG welder. Always consult the manufacturer’s instructions and consult a professional if you are unsure about any repairs or maintenance tasks.
In conclusion, MIG welding is a popular and versatile welding process that offers many benefits, such as high productivity, ease of use, and excellent weld quality. When selecting a MIG welder, it is essential to consider factors such as the type of metal being welded, the thickness of the material, the required output, and the available budget. In addition, proper maintenance and troubleshooting are critical to ensure a MIG welder’s longevity and optimal performance. By promptly following best practices, such as maintaining the welder, using the correct welding techniques, and troubleshooting issues, welders can produce high-quality welds efficiently and safely.
Related Articles:

M Hasan
I’m a professional welder and a writer at heart, so I wanted to share the welding expertise I’ve gathered over the years. In addition, I hope our posts motivate others to start welding. I have well-researched. I promise you’ll find honest advice on choosing the best MIG welder here- www.migweldercart.com
Read My Reviews On The 10 Best Mig Welder.
Disclaimer:
MigWelderCart.com provides content for informational purposes only and does not guarantee the accuracy or reliability of the items featured. We may earn commissions from qualifying purchases through the Amazon Associates Program and revenue from Google AdSense ads. Third-party vendors, including Google, use cookies to serve ads based on prior visits. Users can opt out of personalized ads via Google Ads Settings. All trademarks, brands, and images belong to their respective owners, and usage is at your own risk.